Periodic trends describe patterns in element properties. These patterns appear across the periodic table. Atomic number determines the position of each element. The arrangement of elements explains these trends. Atomic properties change in predictable ways. These trends help explain how atoms behave in reactions.
A Mantra for understanding Important Concepts for Periodic Trends in Chemistry.
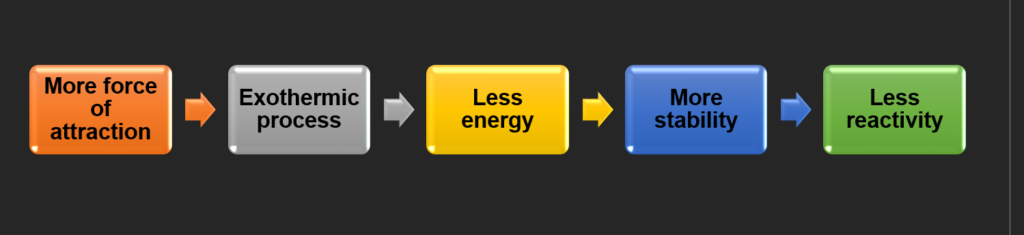
How Force of Attraction Affects Stability, Energy, and Reactivity
When atoms or molecules experience a stronger force of attraction, they naturally tend to move toward a more stable, lower-energy state. As these attractive forces bring particles closer together, the system often releases energy—commonly in the form of heat—making the process exothermic.
This release of energy results in a lower overall energy for the system, which corresponds to greater stability. In chemistry, stability is linked to low reactivity: when a system is already in a favorable, low-energy condition, it has less tendency to undergo further change.
As a result, substances that form strong intermolecular or ionic attractions (such as ionic lattices or polar covalent bonds) tend to be less reactive, since they have little energetic incentive to participate in additional chemical reactions.
Important Concepts for Periodic Trends-Coulomb’s Law-
According to Coulomb’s Law, the magnitude of the force (F) between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges (q1 and q2) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between them. It can be expressed as :
Coulomb’s law can be used for qualitative comparison of attractions among the charged particles in molecules, ions and within the atom etc. Here q1 and q2 are the charges on the particles and r is the distance of separation between the charged particles.
Qualitative Meaning of Coulomb’s law
Meaning of Coulomb’s Law
- More charge → stronger force of attraction.
- Greater distance → weaker force of attraction.
Stronger attraction releases more energy.
Weaker attraction releases less energy.
Force of attraction ∞ Energy(more energy released)
Energy released during attraction is negative.
Stronger attraction lowers energy more.
Lower energy means more stability.
This makes the process exothermic.
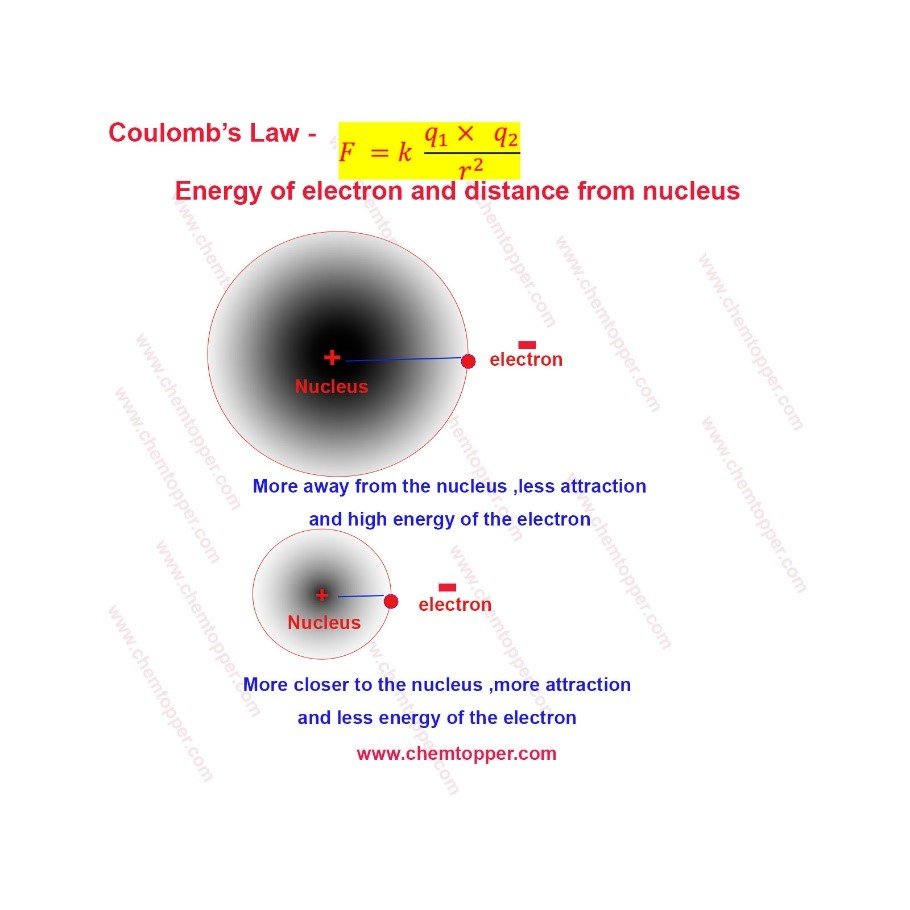
When the distance between the electron and nucleus increases, the attraction decreases.
As a result, the electron has more energy.
On the other hand, when the distance is smaller, the attraction increases.
Therefore, the electron has less energy.
Energy of electron based on Coulomb’s law
One more example of Coulomb’s Law – Force of attractions of ions with water (polar molecule)
Energy of the Electron in an Orbital
Energy of the electron in an orbital depends on a number of factors. These are enumerated below:
1. Important Concepts for Periodic Trends-Distance of the orbitals from the nucleus.
It’s clear from the above picture as the shell number is increasing, distance of the electron from the nucleus increases and hence energy of the electron is increasing as attraction is decreasing.
2. Important Concepts for Periodic Trends-Screening or Shielding Effect
Screening or shielding effect is due to shielding of nuclear charge by inner shell electrons.
More are the number of inner shell electrons; more is the nuclear charge screening and lesser the positive charge felt by valence electrons.
For example, Na has 10 electrons screening its outermost shell electrons and potassium has 18 electrons screening its outermost shell. So, screening effect is more on valence electron of potassium then sodium.
Na -[Ne] 3s1 ; K -[Ar] 4s1
It means valence electron of potassium is less tightly bound to the nucleus due to more screening of nuclear charge and less attraction with the nucleus.
The presence of shielding electrons reduces the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged protons in the nucleus and the outer electrons. Moreover, the repulsive forces between electrons in a many-electron atom further offset the attractive force exerted by the nucleus.
3. Important Concepts for Periodic Trends-Energy Of The Orbitals
Penetration effects of different orbitals can be understood from the probability distribution curves of the electrons in these orbitals. It has been observed that penetration effect follows this order-
More is the penetration effect of the orbitals, more closer is the electron to nucleus which means more attraction between the electron and the nucleus and less energy.
Why the 2s Orbital Is Lower in Energy Than 2p?
At first, it may seem that the 2p orbital should be lower in energy than the 2s orbital.
This is because the 2p electron’s maximum density is closer to the nucleus.
However, a deeper look shows something important.
The 2s orbital has a small hump of electron density very close to the nucleus.
This feature is due to the penetration effect.
As a result, the 2s electron occasionally gets very close to the nucleus.
Even though it usually stays farther out than the 2p electron, it penetrates more often.
Therefore, the 2s electron feels a stronger attraction.
Consequently, the 2s orbital is lower in energy than the 2p orbital.
Penetration Effects and Energy of the Orbitals
From above electron distribution picture, it is can be decided that penetration effect of different orbitals are
3s> 3p> 3d
Greater penetration means more closer to the nucleus and stronger attraction of the electron with the nucleus which means less energy of the electron.
Orbital Penetration and Energy: Why Closer Means More Stable
In general, the more effectively an orbital allows its electron to penetrate through the inner (shielding) electrons and get closer to the nucleus, the lower its energy will be. This is because the stability of an electron is directly related to the strength of its attraction to the nuclear charge. Electrons in orbitals that can approach the nucleus more frequently (like s-orbitals) experience a stronger electrostatic pull, making them lower in energy compared to orbitals like p, d, or f at the same principal energy level.
Do add these these to your Things to Master and you will find that they spin the magic in your understanding of Chemistry.